Innovative Self-Healing Hydrogels: Advances in Tissue Engineering and Wound Therapy
15 10 2024
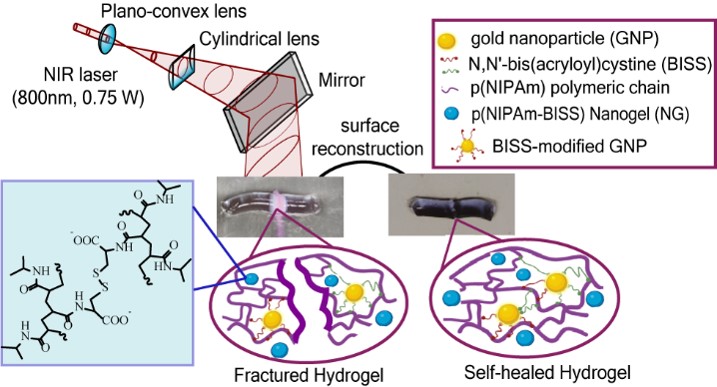
Researchers from the Biological and Chemical Research have developed innovative self-healing hydrogels based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAm). These hydrogels were cross-linked using a newly synthesized cross-linker, N,N’-bis(acryloyl)cystine (BISS). Additionally, the hydrogels have been modified with gold nanoparticles (GNP) and enriched with nanogels (NG) to enhance their properties and functionalities. These advancements suggest promising applications in various fields, particularly in tissue engineering and wound therapy, due to their unique self-healing capabilities and enhanced mechanical properties
Properties and applications
The combination of the photothermal properties of these hydrogels with near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation has led to rapid and nearly complete healing of the material after mechanical damage. The introduction of nanogels into the hydrogel structure significantly increased their drug release capabilities and improved adhesive properties.
Potential applications
The developed materials have great potential for applications in tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound healing processes, which could contribute to the advancement of modern medical therapies.
Link to the article:
Publication information
| Rapid Photoinduced Self-Healing, Controllable Drug Release, Skin Adhesion Ability, and Mechanical Stability of Hydrogels Incorporating Linker-Modified Gold Nanoparticles and Nanogels
Authors: Samaneh Khodami, Mosayeb Gharakhloo, Serife Dagdelen, Piotr Fita, Jan Romanski, Marcin Karbarz, Zbigniew Stojek, Marcin Mackiewicz ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c11908 |
